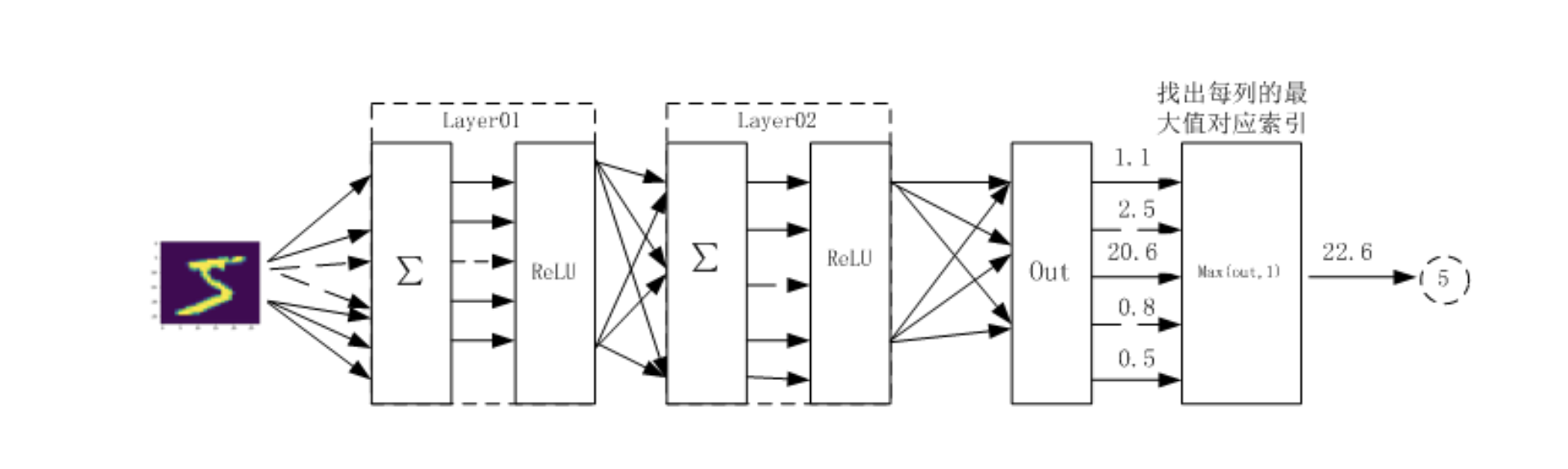
使用Tensor及Autograd实现机器学习
使用Tensor及Autograd实现机器学习
表达式:$y=3x^2+2$
模型:$y=wx^2+b$
损失函数:$Loss=\frac{1}{2}\sum_{i=1}^{100}(wx^2_i+b-y_i)^2$
对损失函数求导:
$\frac{\partial Loss}{\partial w}=\sum_{i=1}^{100}(wx^2_i+b-y_i)^2x^2_i$
$\frac{\partial Loss}{\partial b}=\sum_{i=1}^{100}(wx^2_i+b-y_i)^2$
利用梯度下降法学习参数,学习率为:lr
$w_1-=lr*\frac{\partial Loss}{\partial w}$
$b_1-=lr*\frac{\partial Loss}{\partial b}$
1.生成训练数据
1 | import torch |
1 | torch.manual_seed(100) |

2.初始化权重参数
torch.rand和torch.randn有什么区别?
- torch.rand均匀分布,torch.randn是标准正态分布。
1 | # 随即初始化参数,参数w,b是需要学习的,所以requires_grad=True |
tensor([[0.]], requires_grad=True)
3.训练模型
1 | lr = 0.001 |
4.可视化训练结果
1 | plt.plot(x.numpy(), y_pred.detach().numpy(), 'r-', label='predict') |

tensor([[2.9668]], requires_grad=True) tensor([[2.1138]], requires_grad=True)
1 |
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来自 没有胡子的猫Asimok!
评论