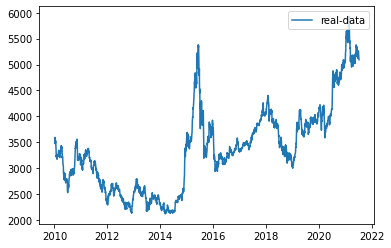
这里采用沪深300指数数据,时间跨度为2010-10-10至今,选择每天最高价格。假设当天最高价依赖当天的前n(如30)天的沪深300的最高价。用LSTM模型来捕捉最高价的时序信息,通过训练模型,使之学会用前n天的最高价,判断当天的最高价(作为训练的标签值)。
导入数据 这里使用tushare来下载沪深300指数数据。可以用pip 安装tushare。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 import tushare as ts cons = ts.get_apis() df = ts.bar('000300' , conn=cons, asset='INDEX' , start_date='2010-01-01' , end_date='' ) df = df.dropna() df.to_csv('sh300.csv' )
本接口即将停止更新,请尽快使用Pro版接口:https://waditu.com/document/2
数据概览 (1)查看下载数据的字段、统计信息等。
1 2 3 4 5 6 print (df.columns) df.describe()
Index(['code', 'open', 'close', 'high', 'low', 'vol', 'amount', 'p_change'], dtype='object')
open
close
high
low
vol
amount
p_change
count
2795.000000
2795.000000
2795.000000
2795.000000
2.795000e+03
2.795000e+03
2795.000000
mean
3342.024819
3344.784845
3370.611827
3314.019947
1.146134e+06
1.499518e+11
0.023324
std
809.944990
810.070118
816.521375
800.923783
8.775841e+05
1.306605e+11
1.448982
min
2079.870000
2086.970000
2118.790000
2023.170000
2.190120e+05
2.120044e+10
-8.750000
25%
2618.540000
2620.265000
2645.770000
2598.400000
6.107925e+05
6.605147e+10
-0.640000
50%
3292.280000
3293.870000
3315.730000
3258.310000
8.908120e+05
1.074772e+11
0.040000
75%
3836.075000
3837.775000
3859.115000
3813.550000
1.344036e+06
1.847992e+11
0.720000
max
5922.070000
5807.720000
5930.910000
5747.660000
6.864391e+06
9.494980e+11
6.710000
(2)可视化最高价数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 import numpy as npdf_index=df.code df_index = df_index.index.tolist() df_all = np.array(df['high' ].tolist()) df=df['high' ]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 from pandas.plotting import register_matplotlib_convertersimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltregister_matplotlib_converters() df, df_all, df_index = readData('high' ) df_all = np.array(df_all.tolist()) plt.plot(df_index, df_all, label='real-data' ) plt.legend(loc='upper right' )
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7fc8a932bfa0>
预处理数据 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 import pandas as pdimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport datetimeimport torchimport torch.nn as nnimport numpy as npfrom torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoaderimport torchvisionimport torchvision.transforms as transforms%matplotlib inline
(1)生成训练数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 def generate_data_by_n_days (series, n, index=False ): if len (series) <= n: raise Exception("The Length of series is %d, while affect by (n=%d)." % (len (series), n)) df = pd.DataFrame() for i in range (n): df['c%d' % i] = series.tolist()[i:-(n - i)] df['y' ] = series.tolist()[n:] if index: df.index = series.index[n:] return df def readData (column='high' , n=30 , all_too=True , index=False , train_end=-500 ): df = pd.read_csv("sh300.csv" , index_col=0 ) df.index = list (map (lambda x: datetime.datetime.strptime(x, "%Y-%m-%d" ), df.index)) df_column = df[column].copy() df_column_train, df_column_test = df_column[:train_end], df_column[train_end - n:] df_generate_train = generate_data_by_n_days(df_column_train, n, index=index) if all_too: return df_generate_train, df_column, df.index.tolist() return df_generate_train
模型 (1)定义模型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class RNN (nn.Module ): def __init__ (self, input_size ): super (RNN, self).__init__() self.rnn = nn.LSTM( input_size=input_size, hidden_size=64 , num_layers=1 , batch_first=True ) self.out = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(64 , 1 ) ) def forward (self, x ): r_out, (h_n, h_c) = self.rnn(x, None ) out = self.out(r_out) return out class mytrainset (Dataset ): def __init__ (self, data ): self.data, self.label = data[:, :-1 ].float (), data[:, -1 ].float () def __getitem__ (self, index ): return self.data[index], self.label[index] def __len__ (self ): return len (self.data)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 n = 30 LR = 0.001 EPOCH = 200 batch_size=20 train_end =-600 device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu' )
(3)训练模型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 from pandas.plotting import register_matplotlib_convertersregister_matplotlib_converters() df, df_all, df_index = readData('high' , n=n, train_end=train_end) df_all = np.array(df_all.tolist()) plt.plot(df_index, df_all, label='real-data' ) plt.legend(loc='upper right' ) df_numpy = np.array(df) df_numpy_mean = np.mean(df_numpy) df_numpy_std = np.std(df_numpy) df_numpy = (df_numpy - df_numpy_mean) / df_numpy_std df_tensor = torch.Tensor(df_numpy) trainset = mytrainset(df_tensor) trainloader = DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 from tensorboardX import SummaryWriterwriter = SummaryWriter(log_dir='logs' ) rnn = RNN(n).to(device) optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(rnn.parameters(), lr=LR) loss_func = nn.MSELoss() for step in range (EPOCH): for tx, ty in trainloader: tx=tx.to(device) ty=ty.to(device) output = rnn(torch.unsqueeze(tx, dim=1 )).to(device) loss = loss_func(torch.squeeze(output), ty) optimizer.zero_grad() loss.backward() optimizer.step() writer.add_scalar('sh300_loss' , loss, step)
(4)测试模型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 generate_data_train = [] generate_data_test = [] test_index = len (df_all) + train_end df_all_normal = (df_all - df_numpy_mean) / df_numpy_std df_all_normal_tensor = torch.Tensor(df_all_normal) for i in range (n, len (df_all)): x = df_all_normal_tensor[i - n:i].to(device) x = torch.unsqueeze(torch.unsqueeze(x, dim=0 ), dim=0 ) y = rnn(x).to(device) if i < test_index: generate_data_train.append(torch.squeeze(y).detach().cpu().numpy() * df_numpy_std + df_numpy_mean) else : generate_data_test.append(torch.squeeze(y).detach().cpu().numpy() * df_numpy_std + df_numpy_mean) plt.plot(df_index[n:train_end], generate_data_train, label='generate_train' ) plt.plot(df_index[train_end:], generate_data_test, label='generate_test' ) plt.plot(df_index[train_end:], df_all[train_end:], label='real-data' ) plt.legend() plt.show()
1 2 3 4 5 plt.clf() plt.plot(df_index[train_end:-500 ], df_all[train_end:-500 ], label='real-data' ) plt.plot(df_index[train_end:-500 ], generate_data_test[-600 :-500 ], label='generate_test' ) plt.legend() plt.show()